An extract from a story set in medieval England:
p.22
A radio show about three great men: p.26
An informal letter: p.32
Three short texts about everyday heroes: p.28
A dialogue taking place in a museum: p.24
2a reading
B.
c (a and b are wrong because they only refer to
certain parts of the text and not the text as a whole)
2a vocabulary & grammar
C.
1. b (‘but many of them looked away. Sir Thomas
was a powerful man... popular.’)
2. c (‘Most of the spectators... that he would defeat Sir
Thomas ...’)
3. c (‘... when Sir Edward appeared ...’)
4. c (‘But Sir Thomas... hit Sir Edward..., ...Sir Thomas fell to
the ground.’)
5. c (‘... fell to the ground in pain. When the prince’s
soldiers removed his armour, they saw that the knight
was wounded.’)
D.
1. d
2. e
3. a
4. f
5. b
6. c
VOCABULARY
PHRASAL VERBS WITH ON AND OFF
1. off
2. off
3. on
4. on
5. off
6. off
7. on
8. on
GRAMMAR
PAST PROGRESSIVE /
PAST SIMPLE VS PAST PROGRESSIVE
A.
1. c 2. a 3. b
B.
1. b 2. a
PRACTICE
1. went
2. were walking
3. saw
4. was wearing
5. was sitting
6. looked
7. wasn’t
8. seemed
9. didn’t know
10. thought
11. were leaving
12. came
2a listening & reading
LISTENING & READING 25
B.
c
C.
1. D (‘Diogenes was sunning himself at the time.’)
2. A (‘Alexander was a powerful man who many people feared.’)
3. N (It is mentioned but it refers to a quality that according to Diogenes, people should have.)
4. D (‘Wasn’t Diogenes the eccentric philosopher...’)
5. A (‘Alexander was a powerful man... He was also very wealthy.’)
6. N
D.
1. b 2. a 3. a 4. c 5. c
2a vocabulary & grammar
VOCABULARY
COLLOCATIONS WITH SAY AND TELL
A.
recognise the difference between their friends and their enemie
B.
1. say thank you
2. tell the time
3. say hello
4. tell the difference
5. tell the truth
6. tell a secret
7. say so
8. telling a story
9. telling a lie
10. saying sorry
GRAMMAR
RELATIVE CLAUSES
A.
Use who or that to refer to people.
Use which or that to refer to things and ideas.
C.
Wasn’t Diogenes the eccentric philosopher who the ancient Athenians admired greatly?
Defining relative clause
Diogenes, who lived in a tub, was only a poor philosopher.
Non-defining relative clause.
PRACTICE
1. Coffee is a drink which many people like to drink in the morning.
2. Saeed Diab, who writes poetry books, is giving a talk at our college.
3. My brother is moving to another city, where he will work as a doctor.
4. Mrs Huda, whose son speaks English very well, is my next door neighbour.
5. Emad, who is captain of the football team, is a friend of mine.
6. Maths is a school subject which many people find difficult.
SPEAKING
King Faisal, whose father was Ibn Saud, was the king of Saudi Arabia.
The Colosseum is the place in ancient Rome where gladiators fought each other.
The Statue of Liberty is a statue which the French gave to the Americans as a symbol of their friendship.
The Tower of London is the place where the Crown Jewels are kept.
Albert Einstein is a man who is famous for his contribution to physics.
2a listening & speaking
LISTENING 34
C.
1. P
2. F
3. P
4. F
5. F
6. R
7. R
SPEAKING
Suggested answer إجابات مُقترحة
SA: I think parents are real heroes. They have to look
after their children and be patient and loving.
SB: Of course. Think about all the responsibility of
raising children. But also, teachers are heroes, don’t
you think?
SC: Yes, they are. They too are responsible for children,
and they have the additional stress of teaching.
SA: I agree, but it’s a very rewarding job. I think I would
love to be a teacher. What about doctors? They save
people’s lives every day.
SB: I think they are very courageous, but I am sure they
are under a lot of pressure, because one mistake
might cost them a person’s life.
SC: It’s also a very stressful job. They deal with diseases
and their job involves working long hours. I wouldn’t
want to be in their shoes, although I admire them
very much.
SA: What do you think about firefighters? They deserve
to be called heroes for sure.
SC: Yes indeed. They enter burning buildings to rescue
people without thinking about the danger their
job involves. I know I could never be a firefighter. I
would be too scared.
SB: No, I disagree. I think I would like the excitement
and also the feeling that I have saved a person’s life.
2a writing
C.
Yes, he does (description: 1st para, reason for
admiring this person: 2nd para, influence: 3rd para)
D.
a. 3 b. 4 c. 2 d. 1
E.
a. strict
b. enthusiasm
c. motivate
d. confident
e. fulfil
f. appreciate
F.
Sp: quiet
WW: last
T: heard
A: a
PR: into
SP: heavy
T: destroyed
2b reading
READING
B.
ba
is wrong because it refers to the archetypical hero of
old ages, whereas the text refers to everyday people who
act as heroes under certain circumstances.
b is the right introduction because it exploits the idea of
the “layman hero”, the everyday person who performs a
heroic act.
c is too general and doesn’t lead into the specific
examples of everyday heroes that the text deals with.
2b vocabulary & grammar
C.
1. M (text 3: ‘rescued his friend after the worst
avalanche in history.’)
2. S (text 2: ‘Was Sameer a super hero? In this case, he was
just very lucky.’)
3. A (text 1: ‘The bookcase was so heavy, I don’t know how
I did it.’)
4. M (Text 3 : ‘ That was the most frightening moment of
my entire life.’)
5. S (Text 2: ‘...survived a terrible train crash and walked
away the only survivor.’)
6. M (Text 3: ‘He was unconscious when I pulled him out.’)
D.
1. b 2. c 3. d 4. e 5. a
VOCABULARY
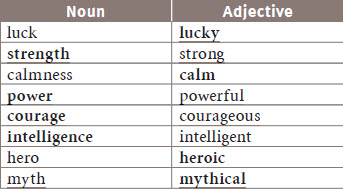
1. WORD BUILDING
B.
1. mythical
2. intelligent
3. powerful
4. strength
5. courageous
2. SIMILES
A.
‘as dark as night’ (3rd text)
‘as white as a sheet’ (3rd text)
B.
as light as a feather, as quiet as a mouse,
as good as gold, as free as a bird, as white as a sheet,
as hungry as a wolf, as quick as lightning, as busy as a bee
1. as free as a bird
2. as hungry as a wolf
3. as busy as a bee
4. as light as a feather
5. as good as gold / as quiet as a mouse
3. WORDS RELATED TO NATURAL
DISASTERS
2b vocabulary & grammar
GRAMMAR
ADJECTIVES – ADVERBS OF MANNER
Violent: adjective
Violently: adverb of manner
COMPARISONS
A.
How are the comparatives and superlatives of
one-syllable adjectives and adverbs formed?
By adding the -er and –est (respectively)
B.
c, a
PRACTICE
1. more exciting
2. the youngest
3. weaker
4. as little
5. more difficult
6. harder
7. farther
8. as quickly
ENGLISH IN USE
1. b
2. c
3. c
4. a
5. b
6. a
7. b
8. c
2b listening & speaking
LISTENING 35
Suggested Answer إجابات مُقترحة
Question 2:
a flat tyre or even more serious mechanical problems run out of petrol (no petrol station in the vicinity) no places to stop and rest
2. Listening
A.
b
B.
1. T
2. F
3. T
4. F
5. T
6. F
SPEAKING
Suggested Answer إجابات مُقترحة
It was a nice day so Bob went horse riding. Bob loved
trains, so he always chose the forest path that led to the
railway track. Unfortunately, as he was riding down a
hill, he fell off the horse and hit his head. He was lying
unconscious on the tracks while his faithful horse went
to get help. Two boys were playing Frisbee nearby and
they came to see what was wrong. They saw a train in
the distance so one of them started waving to stop the
train. The other one managed to pull Bob off the track
and rescue him at the last minute, just as the train was
coming.
2b writing
B.
c
C.
a. Informal language: ...everything is OK at work.;
Not much is happening...; you’ll never guess...;
‘Get out of the way!’; Hope to hear from you soon.; etc.
b. Short forms: ... you’re fine...; ...you’ll never guess...;
...that’s my story
c. Past tenses to narrate events: ...was walking...; ...heard...;
...noticed...; ...was heading...; etc.
d. Time linkers to indicate the sequence of events : while,
as, then, after a while, finally
2b writing
D.
Use while and as with the Past Progressive to
indicate the longer of the two actions which happened
in the past.
Use at first, then and finally to indicate the sequence of
events that happened one after the other.
Use after a while to refer to an event that happened after
some time had passed.
E.
1. While I was driving to work, I had an accident./
I had an accident while I was driving to work.
2. At first, Husam thought something was wrong with the
road, then he realised he had a flat tyre.
3. Afaf was reading a book but after a while she got bored.
4. When I opened the door and saw what a mess the house
was in, I was shocked.
5. The telephone was ringing for a long time and, finally,
somebody answered it.
6. As soon as the head teacher entered the classroom, the
students stopped talking.
2 round-up
VOCABULARY & GRAMMAR
A.
1. c
2. a
3. c
4. a
5. b
6. c
7. a
8. d
9. d
10. d
B.
1. d
2. c
3. d
4. a
5. c
6. b
7. a
8. b
9. b
10. c
C.
1. possessions
2. unselfish
3. unconscious
4. courageous
5. intelligent
6. powerful
7. strength
8. calmness
D.
1. were playing
2. started
3. was working
4. went
5. broke
6. was running
7. were falling
8. saw
9. flew
10. moved
11. ran
12. helped/were helping
13. pulled
14. carried
15. destroyed
E.
1. whose
2. most
3. when
4. When/While
5. more
6. on
7. the
LISTENING 36, 37
1. a 2. c 3. c 4. b 5. a
LISTENING & READING 25
B.
c
C.
1. D (‘Diogenes was sunning himself at the time.’)
2. A (‘Alexander was a powerful man who many people feared.’)
3. N (It is mentioned but it refers to a quality that according to Diogenes, people should have.)
4. D (‘Wasn’t Diogenes the eccentric philosopher...’)
5. A (‘Alexander was a powerful man... He was also very wealthy.’)
6. N
D.
1. b 2. a 3. a 4. c 5. c
2a vocabulary & grammar
VOCABULARY
COLLOCATIONS WITH SAY AND TELL
A.
recognise the difference between their friends and their enemie
B.
1. say thank you
2. tell the time
3. say hello
4. tell the difference
5. tell the truth
6. tell a secret
7. say so
8. telling a story
9. telling a lie
10. saying sorry
GRAMMAR
RELATIVE CLAUSES
A.
Use who or that to refer to people.
Use which or that to refer to things and ideas.
C.
Wasn’t Diogenes the eccentric philosopher who the ancient Athenians admired greatly?
Defining relative clause
Diogenes, who lived in a tub, was only a poor philosopher.
Non-defining relative clause.
PRACTICE
1. Coffee is a drink which many people like to drink in the morning.
2. Saeed Diab, who writes poetry books, is giving a talk at our college.
3. My brother is moving to another city, where he will work as a doctor.
4. Mrs Huda, whose son speaks English very well, is my next door neighbour.
5. Emad, who is captain of the football team, is a friend of mine.
6. Maths is a school subject which many people find difficult.
SPEAKING
King Faisal, whose father was Ibn Saud, was the king of Saudi Arabia.
The Colosseum is the place in ancient Rome where gladiators fought each other.
The Statue of Liberty is a statue which the French gave to the Americans as a symbol of their friendship.
The Tower of London is the place where the Crown Jewels are kept.
Albert Einstein is a man who is famous for his contribution to physics.
2a listening & speaking
LISTENING 34
C.
1. P
2. F
3. P
4. F
5. F
6. R
7. R
SPEAKING
Suggested answer إجابات مُقترحة
SA: I think parents are real heroes. They have to look
after their children and be patient and loving.
SB: Of course. Think about all the responsibility of
raising children. But also, teachers are heroes, don’t
you think?
SC: Yes, they are. They too are responsible for children,
and they have the additional stress of teaching.
SA: I agree, but it’s a very rewarding job. I think I would
love to be a teacher. What about doctors? They save
people’s lives every day.
SB: I think they are very courageous, but I am sure they
are under a lot of pressure, because one mistake
might cost them a person’s life.
SC: It’s also a very stressful job. They deal with diseases
and their job involves working long hours. I wouldn’t
want to be in their shoes, although I admire them
very much.
SA: What do you think about firefighters? They deserve
to be called heroes for sure.
SC: Yes indeed. They enter burning buildings to rescue
people without thinking about the danger their
job involves. I know I could never be a firefighter. I
would be too scared.
SB: No, I disagree. I think I would like the excitement
and also the feeling that I have saved a person’s life.
2a writing
C.
Yes, he does (description: 1st para, reason for
admiring this person: 2nd para, influence: 3rd para)
D.
a. 3 b. 4 c. 2 d. 1
E.
a. strict
b. enthusiasm
c. motivate
d. confident
e. fulfil
f. appreciate
F.
Sp: quiet
WW: last
T: heard
A: a
PR: into
SP: heavy
T: destroyed
2b reading
READING
B.
ba
is wrong because it refers to the archetypical hero of
old ages, whereas the text refers to everyday people who
act as heroes under certain circumstances.
b is the right introduction because it exploits the idea of
the “layman hero”, the everyday person who performs a
heroic act.
c is too general and doesn’t lead into the specific
examples of everyday heroes that the text deals with.
2b vocabulary & grammar
C.
1. M (text 3: ‘rescued his friend after the worst
avalanche in history.’)
2. S (text 2: ‘Was Sameer a super hero? In this case, he was
just very lucky.’)
3. A (text 1: ‘The bookcase was so heavy, I don’t know how
I did it.’)
4. M (Text 3 : ‘ That was the most frightening moment of
my entire life.’)
5. S (Text 2: ‘...survived a terrible train crash and walked
away the only survivor.’)
6. M (Text 3: ‘He was unconscious when I pulled him out.’)
D.
1. b 2. c 3. d 4. e 5. a
VOCABULARY
1. WORD BUILDING
B.
1. mythical
2. intelligent
3. powerful
4. strength
5. courageous
2. SIMILES
A.
‘as dark as night’ (3rd text)
‘as white as a sheet’ (3rd text)
B.
as light as a feather, as quiet as a mouse,
as good as gold, as free as a bird, as white as a sheet,
as hungry as a wolf, as quick as lightning, as busy as a bee
1. as free as a bird
2. as hungry as a wolf
3. as busy as a bee
4. as light as a feather
5. as good as gold / as quiet as a mouse
3. WORDS RELATED TO NATURAL
DISASTERS
2b vocabulary & grammar
GRAMMAR
ADJECTIVES – ADVERBS OF MANNER
Violent: adjective
Violently: adverb of manner
COMPARISONS
A.
How are the comparatives and superlatives of
one-syllable adjectives and adverbs formed?
By adding the -er and –est (respectively)
B.
c, a
PRACTICE
1. more exciting
2. the youngest
3. weaker
4. as little
5. more difficult
6. harder
7. farther
8. as quickly
ENGLISH IN USE
1. b
2. c
3. c
4. a
5. b
6. a
7. b
8. c
2b listening & speaking
LISTENING 35
Suggested Answer إجابات مُقترحة
Question 2:
a flat tyre or even more serious mechanical problems run out of petrol (no petrol station in the vicinity) no places to stop and rest
2. Listening
A.
b
B.
1. T
2. F
3. T
4. F
5. T
6. F
SPEAKING
Suggested Answer إجابات مُقترحة
It was a nice day so Bob went horse riding. Bob loved
trains, so he always chose the forest path that led to the
railway track. Unfortunately, as he was riding down a
hill, he fell off the horse and hit his head. He was lying
unconscious on the tracks while his faithful horse went
to get help. Two boys were playing Frisbee nearby and
they came to see what was wrong. They saw a train in
the distance so one of them started waving to stop the
train. The other one managed to pull Bob off the track
and rescue him at the last minute, just as the train was
coming.
2b writing
B.
c
C.
a. Informal language: ...everything is OK at work.;
Not much is happening...; you’ll never guess...;
‘Get out of the way!’; Hope to hear from you soon.; etc.
b. Short forms: ... you’re fine...; ...you’ll never guess...;
...that’s my story
c. Past tenses to narrate events: ...was walking...; ...heard...;
...noticed...; ...was heading...; etc.
d. Time linkers to indicate the sequence of events : while,
as, then, after a while, finally
2b writing
D.
Use while and as with the Past Progressive to
indicate the longer of the two actions which happened
in the past.
Use at first, then and finally to indicate the sequence of
events that happened one after the other.
Use after a while to refer to an event that happened after
some time had passed.
E.
1. While I was driving to work, I had an accident./
I had an accident while I was driving to work.
2. At first, Husam thought something was wrong with the
road, then he realised he had a flat tyre.
3. Afaf was reading a book but after a while she got bored.
4. When I opened the door and saw what a mess the house
was in, I was shocked.
5. The telephone was ringing for a long time and, finally,
somebody answered it.
6. As soon as the head teacher entered the classroom, the
students stopped talking.
2 round-up
VOCABULARY & GRAMMAR
A.
1. c
2. a
3. c
4. a
5. b
6. c
7. a
8. d
9. d
10. d
B.
1. d
2. c
3. d
4. a
5. c
6. b
7. a
8. b
9. b
10. c
C.
1. possessions
2. unselfish
3. unconscious
4. courageous
5. intelligent
6. powerful
7. strength
8. calmness
D.
1. were playing
2. started
3. was working
4. went
5. broke
6. was running
7. were falling
8. saw
9. flew
10. moved
11. ran
12. helped/were helping
13. pulled
14. carried
15. destroyed
E.
1. whose
2. most
3. when
4. When/While
5. more
6. on
7. the
LISTENING 36, 37
1. a 2. c 3. c 4. b 5. a
عودة لفهرس حلول باقي الوحدات لكتاب الطالب ⇐ {اجابات ترافلر3 كتاب الطالب }